COM3LAB – THE COMPACT ELECTRONICS LABORATORY
3 COMPONENTS BECOME ONE LABORATORY
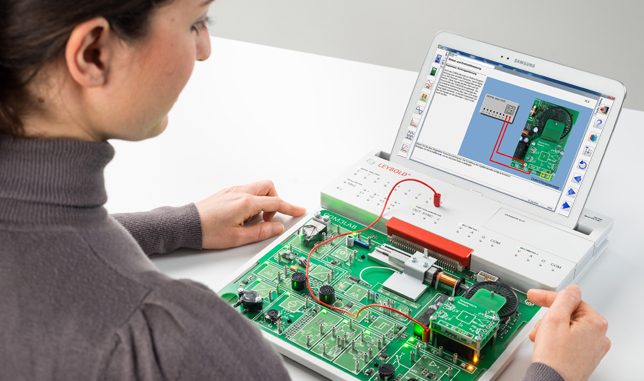
COM3LAB is used for training and further education in electrical engineering and electronics and provides both theoretical and practical knowledge transfer from a single source. The subject matter is not only taught theoretically, but is also deepened by the use of practice-oriented experiments.
COM3LAB consists of a Master Unit and various courses – a course includes an experiment board and learning software. The Master Unit is the basic device via which the software and the experiment board communicate with one another. The COM3LAB learning environment combines experimentation with the advantages of interactive e-learning.
The new Master Unit is the bridge between the experiment board and the learning software. It contains all necessary measuring instruments and power supplies and possesses many significant improvements compared with its predecessors:
- Support for wired and wireless PC interfaces
- Luminous strip makes the system status display visible from a distance
- Anti-theft protection through Kensington lock
- Suitable for inclusive learning through two separate audio outputs
- Support for tablets 2 mm safety sockets and cables
Software:
| No | Courses | Curriculum Coverage | Picture |
| 1 | DC Technology I |
|
|
| 2 | DC Technology II |
|
|
| AC Technology I |
|
||
| AC Technology II |
|
||
| Electronic Component I |
|
||
| Electronic Component II |
|
||
| Digital Technology I |
|
||
| Digital Technology II |
|
||
| Power Electronics |
|
||
| Three Phase Technology |
|
||
| Electro Pneumatic |
|
||
| Control Technology |
|
Video:
[embedyt] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e-oYM2ByOR8[/embedyt]
